Motion in a Magnetic Field
Motion in a Magnetic Field: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Motion of Charged Particle in Uniform Magnetic Field, Radius of the Helical Motion in Magnetic Field and, Pitch of the Helical Motion in Magnetic Field
Important Questions on Motion in a Magnetic Field
A particle having charge of , mass and speed enters a uniform magnetic field, having magnetic induction of , at an angle between velocity vector and magnetic induction. The pitch of its helical path is (in meters)
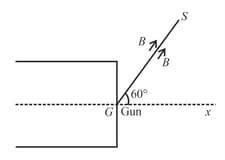
An electron gun G emits electron of energy travelling in the (+)ve x-direction. The electrons are required to hit the spot S where & the line GS makes an angle of with the x-axis, as shown in the fig. A uniform magnetic field parallel to GS exists in the region outsides to electron gun. Find the minimum value of B needed to make the electron hit S.
A proton of mass and charge is moving in a circular orbit in a magnetic field with energy . What should be the energy of ( and ), so that it can revolve in the path of same radius.
In the cyclotron, as radius of the circular path of the charged particle increases ( angular velocity, linear velocity)
In the cyclotron, as radius of the circular path of the charged particle increases ( angular velocity, linear velocity)
A particle of charge and mass moves with a velocity in a magnetic field applied perpendicular to the motion of the particle. The radius of its path in the field is
A proton, a deuteron and an -particle having the same kinetic energy are moving in circular trajectories in a constant magnetic field. If and denote, respectively, the radii of the trajectories of these particles, then
A proton of mass and charge is moving in a circular orbit in a magnetic field with energy . What should be the energy of ( and ), so that it can revolve in the path of same radius.
A particle of charge and mass, moving with a velocity along the -axis, enters the region with uniform magnetic field along the direction. The particle will penetrate in this region in the -direction up to a distance equal to
If a very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge then, the charge experiences no force.
A charge enters a uniform magnetic field at an angle . What will be the path of the charge? Also find its pitch?
A charged particle with the charge to mass ratio enters in a uniform magnetic field at time with velocity . Assume that magnetic field exists in large space. The pitch of the helical path of the motion of the particle is (in meter). Write the value of .
Uniform electric and magnetic fields with strength and induction , respectively, are along axis as shown in figure. A particle with specific charge leaves the origin in the direction of axis with an initial non-relativistic velocity . The coordinate of the particle when it crosses the axis for the time is
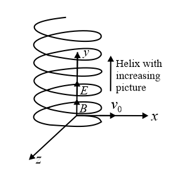
Discuss the motion of a charged particle the uniform magnetic field considering some angle between the magnetic field and velocity of the particle.
The kinetic energy of the emergent proton beam from a cyclotron oscillator having frequency of and dee radius ?
A proton, a deuteron and an -particle with same kinetic energy enter perpendicularly in a uniform magnetic field. Then, the ratio of radii of their circular path is:
An electron of energy describes a circular path in the magnetic field of flux density . The radius of the path is:
The mass of a proton is 1847 times that of an electron. A electron and a proton are injected into a uniform electric field at right angle to the direction of the field with the same initial K.E.
In a crossed field, the magnetic field induction is 2.0T and electric field intensity is . At which velocity the electron will travel in a straight line without the effect of electric and magnetic fields?
An electron enters a region where magnetic field [B] and electric field [E] are mutually perpendicular, then
